By Dimitri Goudis and Brian Birch
Summary: Knowledge Graphs are a different way to store information, making that data easier to read for AI-based tools. This can be a game-changer for small organizations and businesses, so its a good idea to begin by understanding what they are and how they work.
Defining a Knowledge Graph
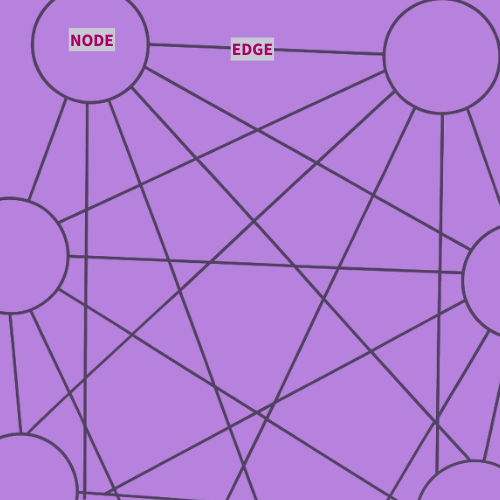
A Knowledge Graph (KG) is a data model that structures knowledge by linking things called “entities” together and defining the relationships, also called “edges” between them. Unlike a traditional database that stores data in isolated tables, a KG captures the context and meaning of the data.
The core building blocks of a Knowledge Graph are:
- Entities (Nodes): These are the “things”, like a customer, a product, a skill, or an event.
- Relationships (Edges): These are the connections between them. For example, “works for,” “is a part of,” or “purchased.”
- Properties: These are additional attributes on the nodes (e.g., a customer’s location) and the edges (e.g., the date of a purchase).
All of this together creates what we call the ontology/schema of a graph database. This gives it visible structure and meaning, and is also what makes it readable by AI. It helps the “machine” reason with information, just like humans do, in complex ways.
Let’s dig into that a little bit more.
How Knowledge graphs enhance AI usage
Generative AI models, especially Large Language Models (LLMs), are excellent at language generation, but they can get confused or simply make things up (called hallucinating). They need as much context as possible, or they try to fill in the gaps with other information they may have been trained on.
Knowledge Graphs provide the context and factual grounding needed to make generative AI more accurate, relevant, and trustworthy.
And the best news? They can be used to help both humans and AI visually and contextually understand complex data faster and more efficiently. Let’s examine that more for real-world settings.
Applications for small nonprofits and businesses
Knowledge Graphs are scalable and can be tailored to an organization’s specific needs, even for smaller teams:
Example 1: Knowledge management
- The problem: Documents, FAQs, product specs, and expert contacts are scattered across file systems, emails, and shared drives.
- Knowledge graph solution: Create an internal “Enterprise Knowledge Graph” that connects all these disparate pieces of information.
Example: An employee can ask a natural language question (e.g., “Who worked on this project last year and what were the challenges?”). The graph finds the connections between people, projects, and documents to provide a precise, consolidated answer.
Example 2: Customer service chatbots
- The problem: Basic chatbots can only answer simple, pre-programmed FAQs. They fail when the question requires combining information or comparison to similar issues.
- Knowledge graph solution: Connect the dots for the AI-powered chatbot, linking key variables (for example, common tech issues customers face, existing bugs, etc.).
Example 3: Event speaker/topic matching and gap analysis
- The Problem: Building a balanced conference agenda is hard, and matching speaker proposals to event themes is often manual and subjective. Organizers may overlook perfect speakers because their proposals didn’t use the exact keywords for a particular track, or they may unknowingly create content overlap (too many talks on one topic) or gaps (no submissions on a key theme).
- Knowledge Graph Solution: Map content and identify synergies, then build a minimal graph that connects the information using structured content (like abstracts and speaker bios). This creates a flexible, objective view of the entire content landscape.
A Knowledge Graph essentially turns complex, fragmented information into a unified area that can be consumed quickly and easily by AI to help solve problems.
Harrier Takeaway
For now, familiarize yourself with the concept of a knowledge graph and do some research about simple use cases for them, and work with your internal staff and favorite GenAI tool (ChatGPT, Gemini, etc.) to explore how you may be able to apply them in the future.
Sources/additional information
- What Are Knowledge Graphs? Benefits, Use Cases & Why They Matter in AI
https://medium.com/@visrow/what-are-knowledge-graphs-benefits-use-cases-why-they-matter-in-ai-55575a17b93b - Knowledge graphs | The Alan Turing Institute
https://www.turing.ac.uk/research/interest-groups/knowledge-graphs - What Is a Knowledge Graph? | IBM
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/knowledge-graph - Knowledge Graphs: What They Are and Why They Matter - Splunk
https://www.splunk.com/en_us/blog/learn/knowledge-graphs.html - Using knowledge graphs to unlock GenAI at scale | EY - US
https://www.ey.com/en_us/insights/emerging-technologies/using-knowledge-graphs-to-unlock-genai-at-scale - Knowledge Graphs: A Must-Have Information Structure for Generative AI - Shelf.io
https://shelf.io/blog/knowledge-graphs-a-must-have-information-structure-for-genera - Generative AI And Knowledge Graphs: A Match Made In Heaven - Forrester
https://www.forrester.com/blogs/generative-ai-and-knowledge-graphs-a-match-made-in-heaven/ - Knowledge Graph Application: A Complete Guide for 2025 - Eliya
https://www.eliya.io/blog/marketing-data/knowledge-graph-application - Knowledge Graphs for Startups: Optimize Time, Costs, and Growth - DevRev
https://devrev.ai/blog/knowledge-graphs-for-startups - Knowledge Graphs: What They Are & Why They Are Important for Search Engines & Small Businesses - Paul Teitelman SEO Consulting
https://www.paulteitelman.com/knowledge-graphs-what-they-are-why-th
.png?width=400&height=120&name=HarrierLogoNew25_400x120_transback%20(1).png)